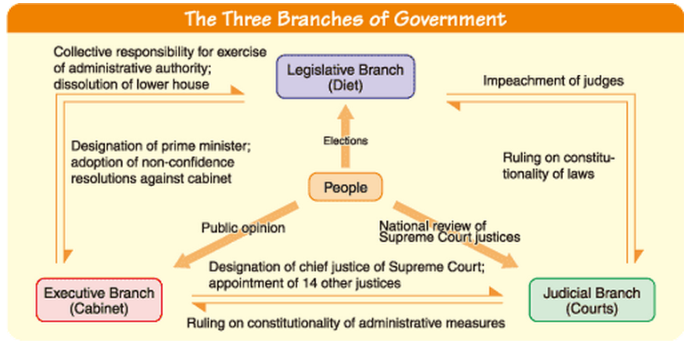
The Structure and Style of Japan's Government
As you'll notice in the graphic below, Japan's government is structured similarly to that of the United State's democratic system. Like in the US, the Japanese people are involved in the nation's political system, although there are some noticeable differences between the two. For example, the Legislative Branch of Japan's government elects the Prime Minister of the Executive Branch. Unlike the Presidential election that the United States holds every four years, instead, the Japanese population elects members into the legislature (called the Diet), and these individuals in turn elect the Prime Minister.
an overview of japan's government
Shinzo Abe- Japan's Prime Minister
The video below touches upon the challenges that Japan's Prime Minister, Shinzo Abe, will face in the future. This short report describes certain governmental and economical issues that Abe will have to deal with in order to get Japan back on the right track. In addition, the video offers some public opinion on the Prime Minister who came to office in December of last year.
The power of the legislative branch

("Japan national diet," 2003)
Japan's legislative system is unique and different compared to the governmental styles of other nations. Follow the link below for a brief summary and explanation of the power and responsibilities of Japan's National Diet.
The National Diet
The National Diet
The Samurai and their Government

("Samurai," 2013)
Like mentioned above, the samurai led Japan's government for many centuries. The link below provides a greater look at the samurai's unique political system, classes, and its eventual abolition. This web page separates the centuries in to different eras to effectively illustrate how the political system evolved over time.
Samurai Government
Samurai Government
Oil and globalization
1. Record:
Oil Production: Japan Produces 5,000 bbl/day.
Oil Consumption: Japan consumes 4.5 million bbl/ day
2. Summarize:
After researching Japan's production and consumption trends using the CIA fact book, I discovered that the nation is the third largest consumer of oil on the planet. In addition, Japan is also the third largest net importer of oil, only being beaten by The United States and China. In total, Japan relies on foreign oil to meet forty-two percent of its energy needs. Despite this large scale consumption trend, Japan has reduced its dependence on oil for energy needs in recent years as the nation has begun to rely more on nuclear power and natural gas. In fact, Japan is the largest importer of liquified natural gas, and is the second largest importer of coal. Japan is the third largest consumer of electricity in the entire world, but it also ranks third in electricity production. Overall, I have found that Japan has very few domestic resources and is forced to rely on imports from foreign countries. Upon further research, I discovered that Japan's large population consumes massive amounts of energy and resources everyday and that this has forced the nation to reevaluate how it consumes and what it produces every year. I would conclude that although Japan is in a rough position in regards to domestic resources, the Japanese population has been starting trends to live more efficient lives to negate the effects of the country's high consumption rates.
("East and southeast," 2013)
Oil Production: Japan Produces 5,000 bbl/day.
Oil Consumption: Japan consumes 4.5 million bbl/ day
2. Summarize:
After researching Japan's production and consumption trends using the CIA fact book, I discovered that the nation is the third largest consumer of oil on the planet. In addition, Japan is also the third largest net importer of oil, only being beaten by The United States and China. In total, Japan relies on foreign oil to meet forty-two percent of its energy needs. Despite this large scale consumption trend, Japan has reduced its dependence on oil for energy needs in recent years as the nation has begun to rely more on nuclear power and natural gas. In fact, Japan is the largest importer of liquified natural gas, and is the second largest importer of coal. Japan is the third largest consumer of electricity in the entire world, but it also ranks third in electricity production. Overall, I have found that Japan has very few domestic resources and is forced to rely on imports from foreign countries. Upon further research, I discovered that Japan's large population consumes massive amounts of energy and resources everyday and that this has forced the nation to reevaluate how it consumes and what it produces every year. I would conclude that although Japan is in a rough position in regards to domestic resources, the Japanese population has been starting trends to live more efficient lives to negate the effects of the country's high consumption rates.
("East and southeast," 2013)
A brief look at Japan's economic structure
Small summary of Japan's economy: Japan has a sommewhat capitalistic market eceonomy that is largely similar to that of The United States. Japan is the world's third largest economy in regards to the nation's GDP and is the fourth largest in terms of purchasing power parity. The nation relies heavily on imports like oil and natural gas. To counteract this, the economy relies greatly on the exportation of automobiles and electronics. In fact, Japan has the world's third largest vehicle industry and the largest electronic goods industry. Similar to The United States, Japan's government does play a role in the nation's economy with things like subsidies and bailouts. Although the marketplace is relatively free, the government does aid in the protection of certain sectors, like the agricultural, to help with production and exportation. As of recent, Japan's economy has been in a recession and the nation is struggling to make it healthy again.
Economic factors: Japan has an unemployment rate of around four and a half percent. This is an interesting statistic because it states that despite the fact that Japan's economy is struggling, individuals are still finding work for the most part. Additionally, Japan's unemployment rate is relatively low in comparison to other major economies like The United States and China which hover at around eight percent and six and a half percent respectively. In addition, Japan has a miniscule consumer price inflation rate of around a tenth of a percent. This incredibly low number ranks Japan as third in the world in regards to inflation, and it significantly beats other economic powerhouses like The United States and China in this area. With China and The United States each having an inflation rate of three percent and two percent respectively, it is evident that Japan's economy is one that still involves consumer spending. I believe that one of the reasons Japan's electronic industry is such a big force in the economy because the price inflation rate is so low and helps keep costs down.
Japan's Gross Domestic Product: Japan's GDP in 2012 was around $36,200.
("East & southeast," 2013)
Economic factors: Japan has an unemployment rate of around four and a half percent. This is an interesting statistic because it states that despite the fact that Japan's economy is struggling, individuals are still finding work for the most part. Additionally, Japan's unemployment rate is relatively low in comparison to other major economies like The United States and China which hover at around eight percent and six and a half percent respectively. In addition, Japan has a miniscule consumer price inflation rate of around a tenth of a percent. This incredibly low number ranks Japan as third in the world in regards to inflation, and it significantly beats other economic powerhouses like The United States and China in this area. With China and The United States each having an inflation rate of three percent and two percent respectively, it is evident that Japan's economy is one that still involves consumer spending. I believe that one of the reasons Japan's electronic industry is such a big force in the economy because the price inflation rate is so low and helps keep costs down.
Japan's Gross Domestic Product: Japan's GDP in 2012 was around $36,200.
("East & southeast," 2013)
Status of women report is located on the cultural and social development page as this is where it was assigned during the course.
Heading Photo Source: (n.d.). Japanese rising sun old flag. [Web Photo]. Retrieved from http://www.stickeruk.co.uk/japan-rising-sun-old-flag-x-6-3825-p.asp